Welcome!
We can be reached at:
Urban Arts Partnership 21 Howard Street - 5th Floor New York, NY 10013
Phone: 212-966-5881
Urban Arts Partnership 21 Howard Street - 5th Floor New York, NY 10013
Phone: 212-966-5881
Fax: 646-966-5911
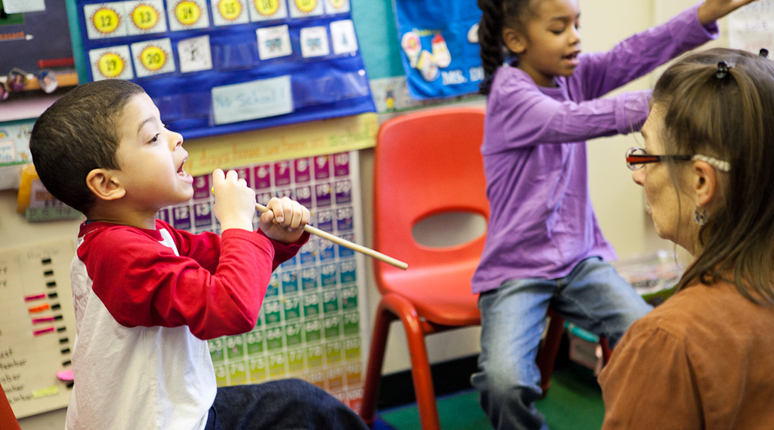
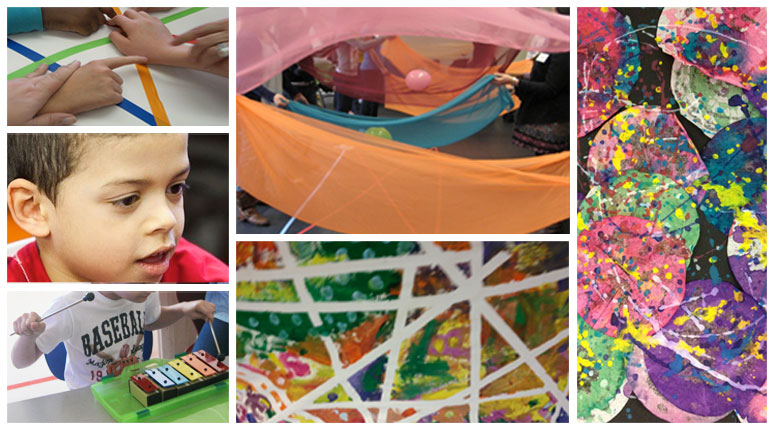
Manhattan New Music Project (MNMP) empowers youth in underserved communities, using the performing arts to develop essential life skills and achieve academic success. We build partnerships among artists, students, teachers and parents that focus on the creation and performance of new works.

 Residency Programs
Residency Programs